Reading time: 3 minutes
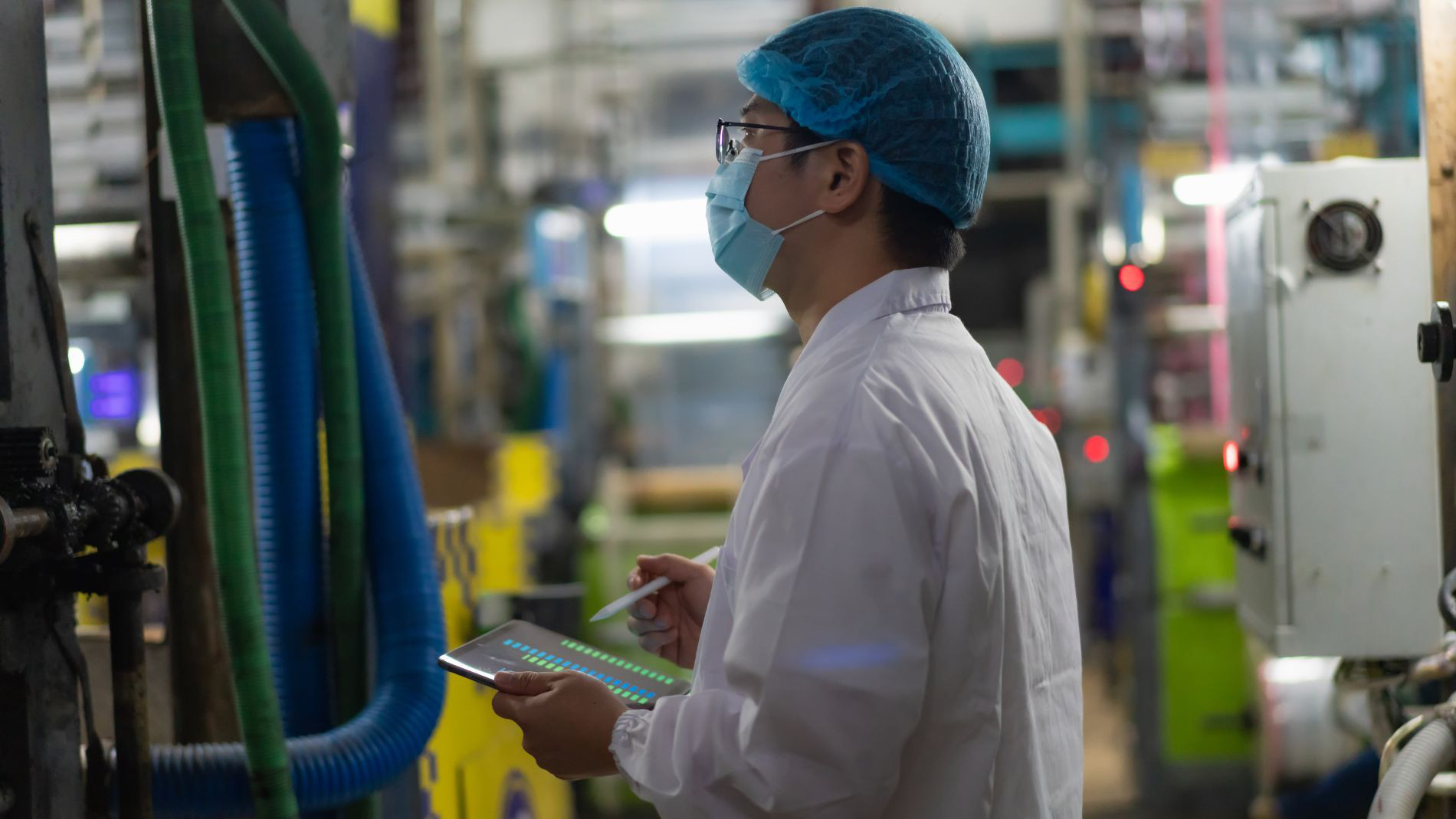

Data is generated along the entire process chain — from slaughtering and cutting to processing, logistics and retail. Sensors and high-resolution camera systems monitor weight, meat quality, and hygiene parameters during slaughtering. In processing and packaging, measurement systems track temperature and humidity to ensure product quality and quickly detect deviations. In storage, sensor technology helps maintain ideal climate conditions and prevents spoilage. On the sales side, smart algorithms analyze sales data to improve demand forecasting, optimize product ranges, and manage supply chains more effectively.
Unlocking Diverse Value Creation Potential
Klaus Schröter, Chairman of the VDMA Meat and Protein Processing Technology Division (German Engineering Federation), sees clear benefits in data usage: “Real-time data allows companies to optimize purchasing, production, and sales. Sensor technologies contribute to more resource-efficient and gentle production and cleaning processes. Additionally, key figures on plant availability help predict and prevent downtimes. Data also enables simulation of process flows, making it a valuable tool for planning and securing investments.”
Process Control and Data Integration at a New Level
Central control systems intelligently link production lines, capture relevant data, and provide real-time access to KPIs. Machine performance indicators such as throughput, quality, and downtimes are collected via standardized interfaces and evaluated to optimize operations — from filling to packaging.
Individual machines also benefit from data collection: parameters such as blade sharpness and wear on slicers help optimize performance and maintain product quality. Modern image processing systems ensure accurate portioning in shape, size, and weight.
Digital Tools in Artisan Operations
Digitalization is increasingly making its way into small-scale businesses. Even artisan butcher shops now automate tasks like mixing complex recipes. Predefined parameters ensure consistency, and ingredient usage is automatically documented. The collected data is seamlessly transferred into enterprise resource planning (ERP) and accounting systems. This reduces administrative effort and simplifies documentation while ensuring consistently high product standards.
Artificial Intelligence as a Game Changer
AI is also gaining relevance in the meat industry. It identifies patterns, recognizes interdependencies, and uncovers optimization potential. Applications include AI-assisted carcass cutting, automated quality control in packaging, and predictive maintenance. Intelligent systems detect packaging defects and sort them out automatically, helping to prevent costly production interruptions.
Herbert Dohrmann, President of the German Butchers' Association, sees potential but also recognizes the challenges: “Many artisan businesses operate with highly individual structures, making AI integration complex—but the overall trend is undeniable.”
Data-Driven Innovation in Packaging Development

Data is also a key driver in developing sustainable packaging materials. Researchers at institutions like the Fraunhofer-Institut für Verfahrendstechnik und Verpackung IVV (Fraunhofer Institute for Process Engineering and Packaging IVV) simulate product shelf life using data such as CO2 concentration inside the packaging to determine material requirements. This enables the development of eco-friendly packaging solutions that maintain product quality. Recyclable materials with functional barriers provide the same level of protection as conventional films. AI also helps determine optimal packaging designs—factoring in shelf life, environmental impact, recyclability, and consumer acceptance.